CO2 emissions from German power mix fluctuated a lot in 2020, storage needed – consultancy
Clean Energy Wire
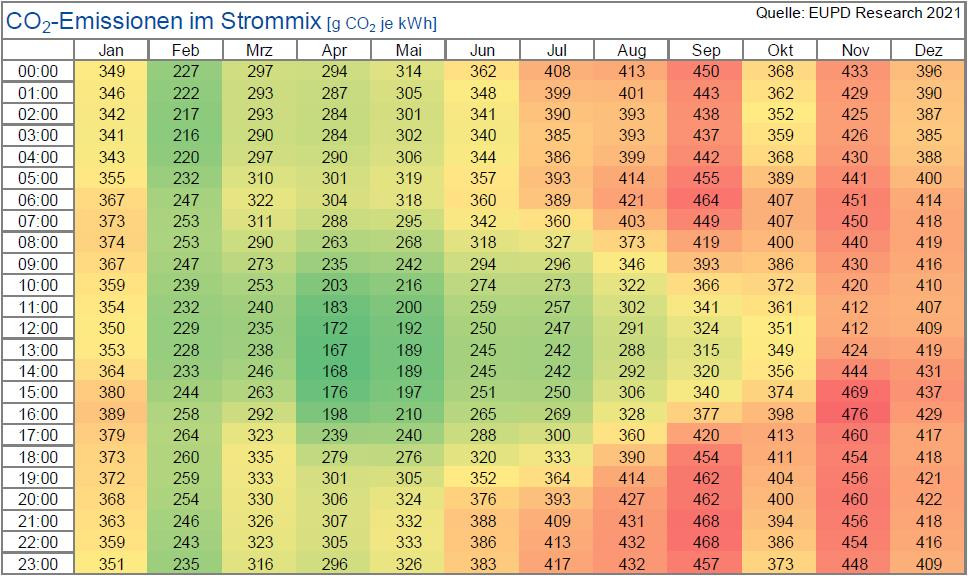
CO2 emissions from the German power mix range between 87 and 664 grammes per kilowatt-hour depending on the time of year and day, researchers from consultancy EUPD Research have found. Their analysis shows that the use of renewable energies, such as wind and solar PV, has considerable impact on greenhouse gas emissions from power generation. In 2020, the month of February saw the lowest CO2 emissions because of very windy weather. During the lunchtime peak in solar PV input, emissions are always at their lowest during a 24-hour day. Despite high solar power generation in the summer months, windless hours before and after sunset caused emissions to go up during the night, when fossil power sources, such as coal and gas, had to be used to secure supply. The researchers who had been commissioned by battery company E3/DC conclude that overall CO2 emissions especially in the winter months can only be lowered “by the comprehensive expansion of [electricity] storage capacities.”
Overall in 2020, about 45 percent of Germany's power was produced from renewable sources, according to preliminary data. Wind supplied almost a quarter of total production, solar 9 percent and biomass 8 percent.