Vote25: 2030 climate and energy targets hinge on next German government
- Contents
- German parties’ energy and climate policy positions for the 2025 election
- Coalition collapse: Tracking the path to Germany's snap elections
- The road to a new coalition government in Germany
- German chancellor candidate Merz must walk fine line between restart and continuity in energy and climate
- Sector previews
- Coalition break-up
- Vote25 - CLEW interview series
- Websites and polling agencies
***Please note: With the election campaign now over, you can find all our reporting on the coalition talks here.***
German parties’ energy and climate policy positions for the 2025 election
CLEW has put together an overview of key parties' energy and climate policy positions from their draft and final election programmes. Find the PDF here.
Coalition collapse: Tracking the path to Germany's snap elections
Germany's coalition government collapsed due to internal disputes over budget and economic policy in November 2024. The country now gears up for snap elections in early 2025, against the backdrop of a flagging economy, the war in Ukraine, and the looming second Trump presidency in the U.S.
This article tracks the latest developments on the road to a new government.
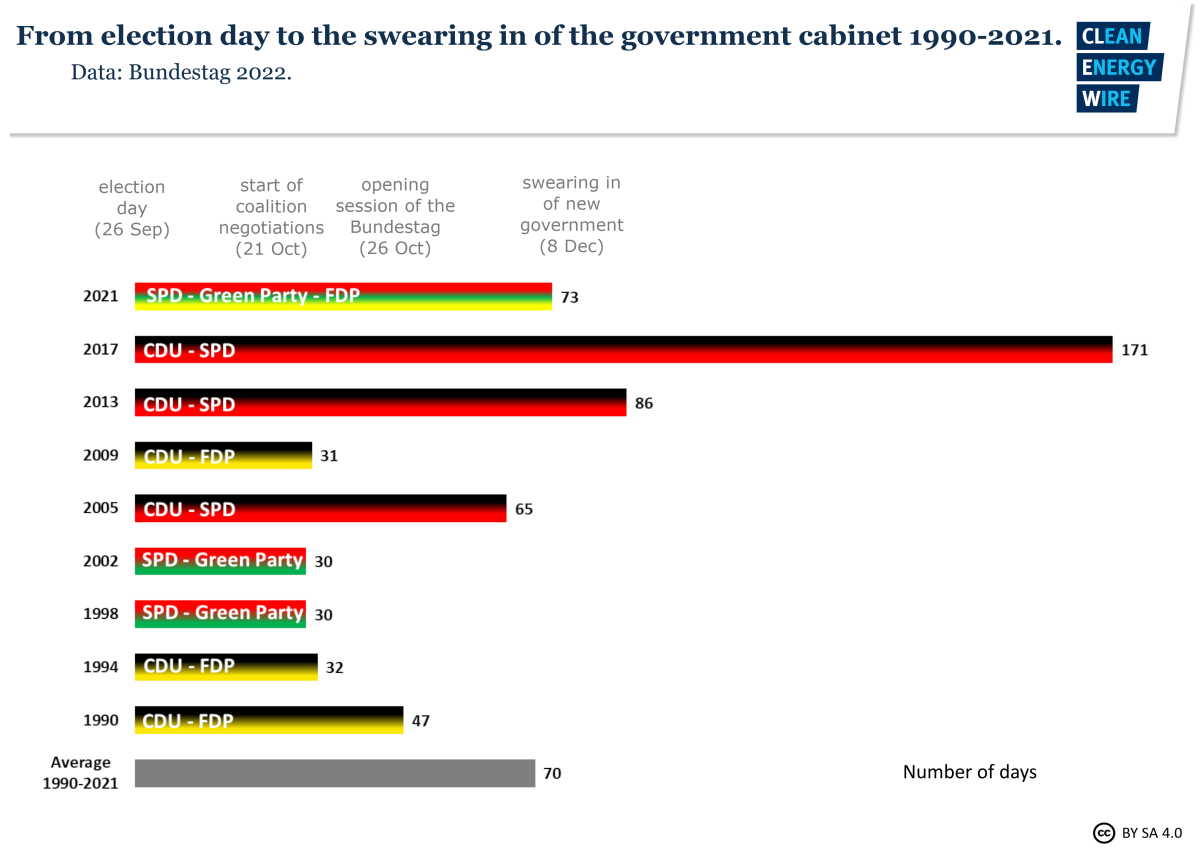
The road to a new coalition government in Germany
Germany looks to be heading for snap elections in early 2025 after chancellor Olaf Scholz's coalition government broke up on 6 November 2024, following months of dispute among the parties. Under normal circumstances, Germans elect a new parliament every four years, and the requirements to initiate an early election are high. Neither the chancellor nor the parliament itself has the power to do this unilaterally, and the process consists of several steps. Eventually, a government is formed after the new federal parliament decides on a chancellor, but the laborious process to negotiate a coalition can last for months after an election.
This factsheet provides a brief overview of the path to the next German government.
German chancellor candidate Merz must walk fine line between restart and continuity in energy and climate
The conservative CDU leader Friedrich Merz is widely tipped to become Germany’s next chancellor – but remains ambiguous on a range of policy fields, notably on energy and climate. Despite being known as a senior policymaker for decades, Merz’s long stint in the private sector not only sets him apart from previous chancellor candidates but also raises a range of questions regarding his priorities as head of government. Many voters regard Merz’s experience in the corporate world as an asset during a difficult time for the German economy. Others are worried that climate action could slide down on the agenda, as the conservative leader seeks to distance himself from the previous centre-left government and its decarbonisation focus. But many industry leaders still are in the dark what Merz plans to do on energy and climate instead. Read the article here.
Sector previews
](https://www.cleanenergywire.org/sites/default/files/styles/paragraph_text_image/public/paragraphs/images/world-economic-forum-donald-trump-annual-meeting-2025.jpg?itok=DpgR-FmG)
Next German government must shape unified EU response as Trump shakes global order
As the new U.S. administration under president Donald Trump upends decades of transatlantic relations and the wider geopolitical order, Germany faces the challenging task of resetting relations with its neighbours to ensure a strong EU role in the world. Increasingly taking control of its own defence, helping to tackle global climate change, and ensuring energy security all require an assertive next government after the snap election on 23 February. The conservatives are likely to lead the next pro-European coalition that supports the European Green Deal in general, but could try to weaken certain elements in an effort to ensure competitiveness of German businesses, experts say. Read the article here.
Climate adaptation financing must find new footing in next German legislative period
Germany's outgoing government made important moves to protect the country against the worsening effects of climate change. Notably, it introduced the first legally-binding climate adaptation law and presented a strategy to protect people and infrastructure against increasingly severe weather events. However, Germany's next government after the snap election still has to overcome key challenges like funding and knowledge gaps to implement measures at a local level. Read the analysis here.

Next German government must reconcile industrial decarbonisation and competitiveness
As Germans prepare to head to the polls for the 23 February snap election, the weakness of the country’s large industrial base has become a campaign focus. Some opposition policymakers blame exaggerated climate policies for the troubles at sector giants like VW and many energy-intensive companies. But most experts and businesses agree that the new government must push forward industry decarbonisation despite tight budgets in close cooperation with the EU. A delay would only put long-term competitiveness in future markets at risk, they warn. Read the full analysis.
Keeping homes affordable while making them climate-friendly is next German govt's big challenge
Making German homes less climate-damaging and keeping them affordable for residents at the same time will be a central task for the country's next government. The heated controversy over a phaseout law for oil and gas boilers is still fresh on people's minds, and populist parties have successfully capitalised on anxious voters' concerns that they won't be able to afford the transition to a cleaner future. However, cutting heating emissions has become urgent - Germany is already set to miss the corresponding 2030 climate targets as it continues to rely on fossil fuel boilers, while energy-saving renovations proceed at a glacial pace. Read the analysis here.

Transport transition poses policy conundrum for next German government
Germany’s next government will inherit a major policy predicament: How can it finally initiate serious transport emission cuts against a backdrop of tight finances, a struggling car industry, and a crumbling transport infrastructure? After years of foot-dragging under previous governments, the mobility sector is lagging far behind in the country’s landmark energy transition, meaning major policy shifts are required as 2030 climate targets move into view. Read the analysis here.
Mixed climate legacy of Scholz’s collapsed coalition leaves challenges for next government
The early end of Olaf Scholz’s coalition government follows a three-year term marked by crises and a deep internal dispute over funding for future climate and energy policies. Despite its noisy demise, the chancellor’s three-party alliance has made significant progress in key policy areas, such as renewables expansion. But the many funding questions and policy loose ends left behind by the coalition’s collapse will not make the job easier for a new government after the election in February 2025. It faces economic woes, security challenges and mounting costs that could challenge the acceptance of climate policies. Read the article here.
Coalition break-up
Q&A: What does the German coalition government break-up mean for climate and energy?
Germany's coalition government under Olaf Scholz has come to an early end – on the day Donald Trump won the U.S. presidential election. The chancellor sacked his finance minister after long internal disputes over the right way forward on economic recovery and the energy transition. The break-up now leaves the country with a host of unfinished policy proposals that risk grinding to a halt until a snap election is held and a new government is sworn in next year. This includes urgent matters such as Germany's 2025 budget, without which many climate, energy, and industry support programmes could be left hanging in the balance for months, unless a minority government manages to forge new majorities in parliament. Read the factsheet here.
Reactions from energy and climate community to collapse of Germany’s coalition government
Following the break-up of Germany's governing coalition, the country's energy industry urged rapid snap elections to give companies much-needed investment security in uncertain times. Youth climate movement Fridays for Future announced nationwide demonstrations to ensure climate topics are central to election campaigns. Read the article here.
Vote25 - CLEW interview series
In the run-up to the snap election on 23 February, Clean Energy Wire interviews key actors in the German climate and energy debate to find out about their expectations regarding the vote as well as other events coming up in 2025.
Far-right AfD shifts debate on German climate policy, but lacks real say – researcher
The far-right Alternative for Germany (AfD) – the second strongest polling party ahead of Germany's snap elections on 23 February – is the only major party to outright reject the scientific consensus behind human-induced climate change. The AfD will likely remain in opposition for the coming term, yet the party's growing strength has influenced the electoral campaign through agenda-setting, says political scientist Manès Weisskircher. While some of their anti-climate protection messages have found support in the wider population, their fundamental criticism of climate action relies on exaggerated claims and leaves nuance out of complicated policy decisions, the researcher who focuses on far-right politics and climate protection at TU Dresden told Clean Energy Wire. Still, a growing support base means other mainstream parties might turn quieter on their climate ambition, Weisskircher warned. Read the interview here.
Snap election chance for Germany to reset relations with European partners – analyst
Germany’s snap elections on 23 February take place against the backdrop of massive changes in geopolitics, presenting the next government with the opportunity to reset its relationships with major European partners, says Rafael Loss, security policy analyst at the European Council on Foreign Relations (ECFR). The country’s approach to tightly coordinate actions with the U.S. – from rethinking its energy policy to rebuilding its armed forces, and military aid to Ukraine – is no longer sustainable with Donald Trump in the White House, the researcher says. There is a risk that Trump will try to play EU states off against each other, so Germany must manage to identify and communicate its own interests, but see how these can serve a broader European interest. Ideally, Europe would show a more consolidated effort to diversify and strengthen energy relations going forward, Loss told Clean Energy Wire in this interview.
Next German government should focus on EU cooperation in industry decarbonisation - researcher
Slowing down industry decarbonisation in Germany would result in a dangerous loss of competitiveness in emerging green markets, says Philipp Verpoort, a researcher at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK). Instead, the next German government needs to provide companies with clarity over the country's long-term policy for climate-friendly investments and focus on European cooperation to make the process more affordable, Verpoort told Clean Energy Wire. The physicist is also the lead author of a recent report by the country’s government-funded Ariadne energy transition research alliance, which warned Germany against relying on future long-distance green hydrogen imports in its drive to reduce emissions in the steel and chemicals industries. Read the interview here.
](https://www.cleanenergywire.org/sites/default/files/styles/paragraph_text_image/public/paragraphs/images/un-climate-change-kiara-worth-bilateral-un-sec-gen-guterres-german-delegation-jennifer-morgan.jpg?itok=et-kWGl6)
Next German govt should cooperate beyond UN on climate, set realistic expectations – researcher
As geopolitical tensions escalate and make UN climate negotiations increasingly difficult, the next German government should continue to explore alternative alliances to push for decarbonisation, says Marian Feist, senior research fellow at the Hertie School’s Centre for Sustainability. Such attempts cooled off in recent years, and Germany should learn from mistakes of the past, setting realistic expectations from the outset. However, Scholz’s outgoing coalition government did well to put the foreign office in charge of climate diplomacy, as it has allowed the country to act more assertively on the international stage, Feist says in this interview.
Next gov't must bring Germany to digital age to enable flexibilisation – energy market association
The next German government must achieve what the previous few have not: increasing digitalisation, says Robert Busch, managing director of the Association of Energy Market Innovators (bne). Electricity system flexibility can only be achieved through fully digitalised processes, so Germany must get the smart meter rollout off the ground by radically simplifying the requirements, Bush argued. Future security of electricity supply should stem from power plants themselves, instead of the government paying them to stand at the ready, the lobby group leader told Clean Energy Wire in this interview.
Germany must embrace transformation, seek European approach to industry crises – researcher
Germany is of central importance when it comes to the EU defining its priorities in energy and industrial policies, says Simone Tagliapietra, senior fellow at Brussels-based think tank Bruegel. He argues that the country’s next government must avoid focusing on national strategies to tackle its myriad crises, and instead work to deepen the European energy union. Only a stronger European energy union could help to lower prices, Tagliapietra told Clean Energy Wire in this interview. Germany is not the anchor of stability it once was and its superiority in some technologies – including the key automotive sector – is under threat, Tagliapietra warns in this interview.

Next German gov’t must tap into renewables’ potential for ‘Dunkelflaute’ backup capacities - BEE
The collapsed coalition of chancellor Olaf Scholz achieved a few important breakthroughs for Germany’s energy transition that should not be sacrificed for point-scoring in election campaigns, says Wolfram Axthelm from the Renewable Energy Federation (BEE). The renewable power industry lobby group’s managing director argues that worries over electricity supply security in Germany are unfounded even if the coalition’s break-up prevented the adoption of key regulation and warns that developments at the EU level and in the U.S. must not be overlooked in the run-up to Germany’s snap elections. Read the interview here.
Next government must use transport transition to shore up competitiveness – think tank
Germany’s next government must focus on the shift to climate-friendly mobility to secure industry competitiveness and ensure a socially just energy transition, says Christian Hochfeld, director of green mobility think tank Agora Verkehrswende, which has published an assessment and outlook of the country’s transport policies. He says the incoming government must approach the transition not only as a climate or transport project, but as a joint endeavour that also benefits industrial and social policy. The outgoing government scored some successes in the mobility sector, but overall progress remained patchy, Hochfeld argues in this interview.

Construction of new gas power plants must be top priority for next government - energy industry
Ensuring the timely construction of new hydrogen-ready gas power plants must be a top priority in energy policy for Germany's next government, says the head of the German Association of Energy and Water Industries (BDEW). Lobby group leader Kerstin Andreae warns that general power supply security as well as the country's coal power phase-out ambitions hinge on an immediate adoption of the related Power Plant Security Act, in order to give investors legal clarity before the beginning of the new year. The former member of parliament for the Green Party argues that party politics must not put the country's grid stability at risk, and urges policymakers from all parties to respond to technical necessities in the energy system by finding compromise on key issues before the 2025 elections. Read the interview here.
Affordability of transition is key topic for next government – researcher
The break-up of Germany's coalition government could further undermine public acceptance of the energy transition's costs, warns Brigitte Knopf, head of the think tank Zukunft KlimaSozial, which focuses on climate policy's social aspects. The researcher, who also co-leads the government’s Council of Experts on Climate Change, says the next government urgently needs to address the financial impact on households of including heating and transport in EU emissions trading. But Knopf warned that a reversal of climate policies, such as Germany’s controversial heating transition law, would only add uncertainty and costs. Find the interview here.
Geopolitical instability could undermine climate commitments in 2025, warns German env agency
Next year will be a difficult one for climate policy, says Susanne Dröge, head of climate protection and energy at the Federal Environment Agency (UBA). Governments will have to show whether they are still committed to strong climate action amidst a challenging geopolitical environment, Dröge told Clean Energy Wire. Yet inaction risks jeopardising progress and inducing higher costs. In Germany, reducing emissions in buildings and transport remains the toughest nut to crack. Meanwhile, the country is now at the forefront of the climate adaptation debate, Kirsten Sander, scientific policy advisor at UBA, added in this interview.
Next gov't must solve climate adaptation financing challenge as topic gains traction – think tank
Germany made significant progress in the area of climate adaptation in the past legislative period, said Andrea Fischer-Hotzel from the German Institute of Urban Affairs (Difu). From the national to the municipal level, there is now awareness of the need to better prepare the country to deal with heatwaves, storms and drought, the researcher told Clean Energy Wire. However, even though Germany now has a legally-binding framework for climate adaptation measures, financing them remains an unresolved issue. Beyond climate adaptation, Germany must speed up efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to reach future climate targets, her colleague Björn Weber said in this interview.
Websites and polling agencies
- Bundeswahlleiter.de
The latest official information on the elections can be found on the English language website of the Federal Returning Officer. The site offers an election glossary, explaining terms like "overhang mandates", "Sainte-Laguë/Schepers", and "proportional representation". After the elections, the website will present the official results. - Wahlrecht.de
A group of students established poll tracking website Wahlrecht.de as an independent, non-party, non-commercial website on election topics, electoral systems, the right to vote and opinion polls for federal and state elections. Parts of the site are in English, but most information is available only in German. Here you can find a list of the latest poll results by Germany’s large polling agencies. - pollytix strategic research
pollytix offers a visualisation of trends in Germans’ party preferences in opinion polls, and a coalition calculator. - Polling agencies
forsa, Forschungsgruppe Wahlen, infratest dimap, INSA-CONSULERE, Institut für Demoskopie Allensbach (IfD), Kantar Emnid, YouGov