Germany's electricity grid stable amid energy transition
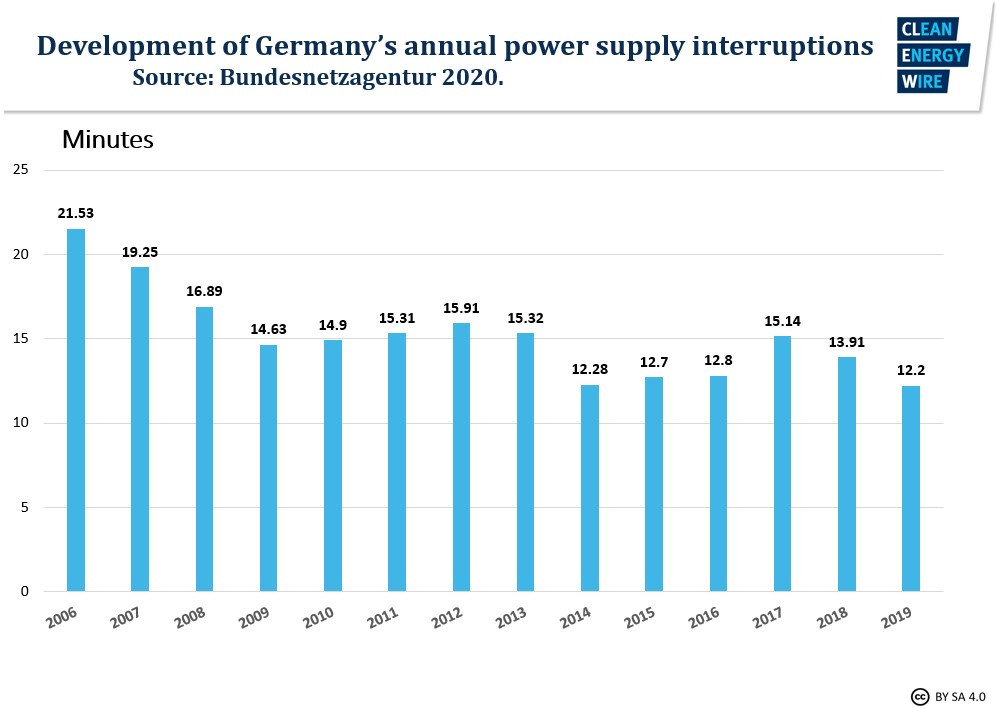
Germany’s power grid stability and security of supply has been stable over recent years despite a huge expansion of intermittent green electricity production. Average power outages per consumer amounted to 12 minutes in 2019, a slight decrease from almost 14 minutes in 2018, according to the Federal Network Agency (BNetzA).
"The energy transition and the rising share of decentralised generating capacity continue to have no negative effects on the quality of supply," the agency said in 2020. The slightly higher level of interruptions in 2017 (a little over 15 minutes) was caused by extreme weather events like storms, floods and snow, rather than the energy transition. "Interruption times in the distribution network caused by weather events more than doubled compared to a year earlier," the BNetzA said of 2017 compared to 2016, where outages averaged less than 13 minutes per consumer.
When systematic monitoring started in 2006, average outage times exceeded 20 minutes (see graph). In the same period, the share of renewable electricity production in Germany rose from 11.3 to 33.1 percent, mostly from fluctuating sources such as wind and solar power stations.
The statistic is based on the international “System Average Interruption Duration Index” (SAIDI), which measures the total duration of electricity blackouts longer than three minutes for the average customer.
Germany's security of supply is among the best in Europe, according to the Council of European Energy Regulators (CEER). In the CEER's 2018 comparison of 2016 figures, the country’s SAIDI score including exceptional disruptions ranked second in the European Union. Only Switzerland fared better. By contrast, the UK, France and Spain each had around 50 minutes of disruptions per year. Romania had the longest interruptions, averaging 371 minutes.
Globally, Germany also fares very well. US citizens on average went without power for an average of almost eight hours in 2017, according to the US Energy Information Agency (EIA). In Western Australia's three grids, the SAIDI score was 152, 59 and 410 minutes in 2017-18.
Generally, security of supply strongly correlates with the share of underground electricity cables. In Germany, more than 80 percent of its 1.8 million kilometres of cables are buried, whereas in the US – with around 40 percent – and Australia and many Southern European countries, this share tends to be lower. This makes the grid more vulnerable to being disrupted, for example by fallen tree branches.
The sources of energy generation so far have little impact on security of supply. But grid operators in Germany have to go to great lengths to balance asymmetric production of green electricity across their networks. The amount of so-called “re-dispatch measures” has risen strongly. Redispatch is when the grid operator forces a power station to lower production in a region with oversupply, and directs another plant in a low-production region to higher output. The cost is passed on to consumers.
For more details on Germany's electricity network, read the dossier The energy transition and Germany’s power grid and the factsheets Re-dispatch costs in the German power grid and Set-up and challenges of Germany's power grid.